If you had sold it for less than its book value, you would have recorded a loss. When an asset is sold for less than its Net Book Value, we have a loss on the sale of the asset. When an asset is sold for more than its Net Book Value, we have a gain on the sale of the asset. As an example, let’s say our example asset is sold at the end of Year 3 and that we used Straight Line depreciation for this asset. For example, on December 31, we dispose of 10 office computers that have reached their useful life of 3 years. Each computer has the cost of $1,700 on the balance sheet, in which its residual value has been estimated to be $200 at the start of the depreciation.
Methods of Fixed Asset Disposal
What’s more, capturing important info like the date of disposal, sales price, and reason for disposal can give valuable insights. To do this, implement procedures and controls, like assigning personnel and software to simplify the recording process. Understanding the meaning of asset disposal and write-off can be challenging for individuals new to accounting. That said, knowing the differences between the two concepts can help eliminate any confusion. Additionally, they must check whether they eliminated all records of the assets from their books to finish the process.
- It reflects the reduction in value of an asset due to factors such as usage, aging, or technological obsolescence.
- In our example, selling the machinery for $25,000 when its book value is $20,000 results in a $5,000 gain.
- If there is a difference between disposal proceeds and carrying value, a disposal gain or loss occurs from a company’s financial records.
- It’s also about navigating a maze of legal requirements and compliance issues.
- Accurate journal entries for these transactions ensure that financial statements reflect the true financial position of the business.
- •Recording any consideration (usually cash) received or paid or to be received or paid.
Ledger Entries for Disposal of Fixed Assets
- Continuing with the previous example, a credit entry of $50,000 would be made to the machinery account, which corresponds to the asset’s historical cost.
- Free accounting tools and templates to help speed up and simplify workflows.
- Managing the disposal of IT assets is more than just a spring cleaning exercise.
- There are two circumstances under which it will be necessary to record the disposal of an asset.
- Some businesses trade in old assets to receive a discount on the purchase of a new asset.
- Understanding how to record depreciation and the disposal of fixed assets is essential for accurate financial reporting and maintaining the integrity of financial statements.
These ratios are often scrutinized CARES Act by investors and analysts to gauge the efficiency and profitability of a company, making accurate asset disposal entries indispensable. When a company decides to dispose of an asset, it must first ensure that the asset’s removal from the company’s books is timely and reflects the transaction’s actual date. This involves reviewing the asset’s ledger to confirm the historical cost and the accumulated depreciation to date.
Related AccountingTools Courses

This journal entry is made to remove the fixed asset from the balance sheet when it is fully depreciated. This is usually done when we no longer have a use for it in the business. Additionally, we simply discard the fully depreciated asset in this journal entry, so no sale transaction is involved here. When an asset is HOA Accounting determined to no longer be of use, it is removed from the financial statements through a process called write-off. This requires a specific journal entry that impacts both the balance sheet and the income statement. In managing a company’s assets, keeping accurate and detailed records is essential to ensure financial statements reflect the real value of the company’s resources.
Properly recording asset disposal journal entries is a crucial aspect of financial management. It ensures that the company’s books accurately reflect the current state of its assets and liabilities, which is essential for maintaining transparency and compliance with accounting standards. The next component of the journal entry involves recording any cash received from the disposal. The amount recorded should be the actual cash received from the sale or disposal of the asset. If the machinery was sold for $25,000, the cash account would be debited by this amount. This debit entry increases the company’s cash balance and is essential for accurately reflecting the inflow of funds resulting from the disposal transaction.
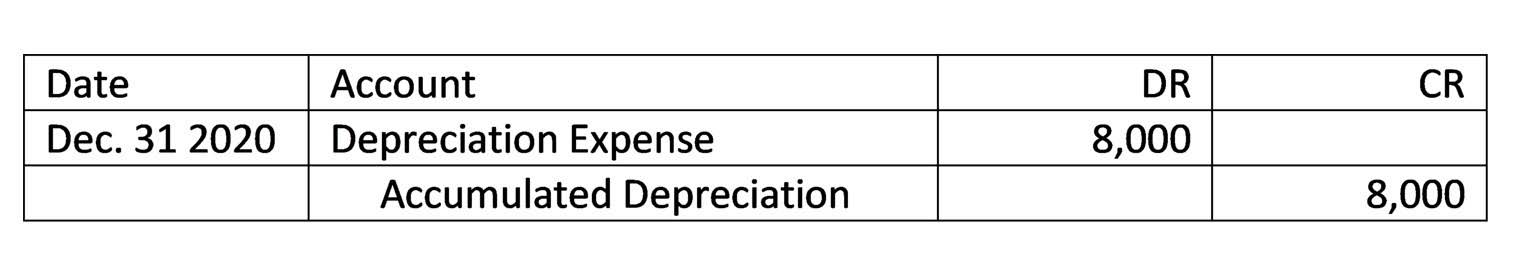
Depreciation is the systematic allocation of the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life. It reflects the reduction in value of an asset due to factors such as usage, aging, or technological obsolescence. If you’d like to practice these three types of disposals, click here to access the free Financial Edge template which contains three mock scenarios of asset disposals. In most cases you’ll need to calculate an asset’s depreciation so you can record its disposal value on your books. Most businesses have multiple types of assets, like inventory, vehicles, and equipment, that help them bring in revenue how to record disposal of asset and add value to the business. A long-term asset will likely have a new value yearly owing to depreciation.


Remember, the way you handle the end of your IT assets’ lifecycle is just as important as how you manage their beginning. In conclusion, a company can make fixed asset disposal for different reasons. The difference between the book value of the asset and the sale price upon disposal determines whether the company realizes a profit or incurs a loss from the transaction.
- In other words, it’s part of keeping your accounting records up to date.
- This information is important for the entity as it helps to portray the financial performance of the entity accurately.
- This not only helps with compliance but also with managing your company’s resources effectively.
- Properly recording the disposal of fixed assets in ledger accounting ensures accurate financial reporting and helps determine gains or losses from asset sales.
- Additionally, it’s important to remove the asset and its accumulated depreciation from the balance sheet.
- For example, if an asset is bought for £500m with an estimated useful life of 100 years and a residual value of £300m, the depreciable amount totals £200m.
- PwC refers to the US member firm or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates, and may sometimes refer to the PwC network.
Missteps in this area can lead to inaccurate financial statements, affecting decision-making processes and potentially leading to regulatory issues. The disposal of an asset also affects the cash flow statement, which tracks the inflows and outflows of cash within a company. The proceeds from the sale of an asset are reported as an inflow of cash in the investing activities section of the cash flow statement. This reflects the liquidation of a long-term asset and its conversion into cash or cash equivalents. The reporting of this cash inflow provides insight into how the disposal has impacted the company’s liquidity and may affect its ability to fund operations or invest in new opportunities. A business may donate fixed assets to charities, educational institutions, or government agencies.
What is a Contra Account?
If an asset reaches the end of its life or is no longer used, recording the disposal of the asset is important in making sure your accounting records are up to date. Also, if a company disposes of assets by selling with gain or loss, the gain and loss should be reported on the income statement. At the end of the third year, the machinery is fully depreciated, and the asset must be disposed of. For example, state agencies, banks, and other businesses utilize this form to monitor their assets.







